 What is Hydrocephalus?
What is Hydrocephalus?
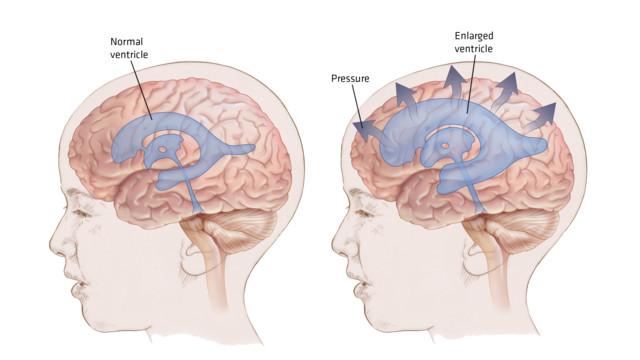
Hydrocephalus is a condition that occurs when cerebrospinal fluid, or “CSF”, builds up in the cavities—ventricles—in the brain, causing it to swell. It is a complex disorder most common in young children and adults over 60 years old. The name itself means “water on the brain”. Brain damage can occur as a result of CSF buildup, possibly leading to developmental, physical, and intellectual impairments. Hydrocephalus requires treatment to prevent serious complications.
Hydrocephalus Treatment
Hydrocephalus has several treatment options, but the most common is to surgically implant a shunt. A shunt is a drainage system made up of a long tube with a valve. The shunt ventricular catheter is inserted in the brain’s ventricles to drain and redirect the excess fluid into another part of the patient’s body. The valve helps CSF flow at a normal rate in the right direction. Excess fluid drains from the brain and out the other end of the tube, where it can be more easily absorbed. All components of the shunt system are implanted (placed) under the skin and must be monitored regularly.

